These cells are involved in adaptive immunity. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia accounts for approximately 70% of all childhood leukemia cases (ages 0 to 19 years), making it the most common type of childhood cancer.
Of the 2,200 samples, 70 were previously collected from confirmed pcr positive patients.
T cell versus b cell. Principles and practice, 3rd ed., elsevier, ch. B cells mature in the blood stream. I think in the adult world, the main difference there is that based on the french.
The development of dormancy in memory t cells, b cells, and plasma cells is a natural temporal evolution after infection and/or vaccination that produces populations that can rapidly be activated. Of the 2,200 samples, 70 were previously collected from confirmed pcr positive patients. Like all blood cells, they are made in the bone marrow.
They are a type of lymphocytes. While b cells produce the antibodies that target diseased cells, t cells directly destroy bacteria or cells infected with viruses. Target recognition stephen nutt, sebastian carotta, axel kallies clinical immunology:
T cells, much like b cells, are vital to our immune system. The role of t cells in igg production; Production of antibodies t cells do not produce antibodies.
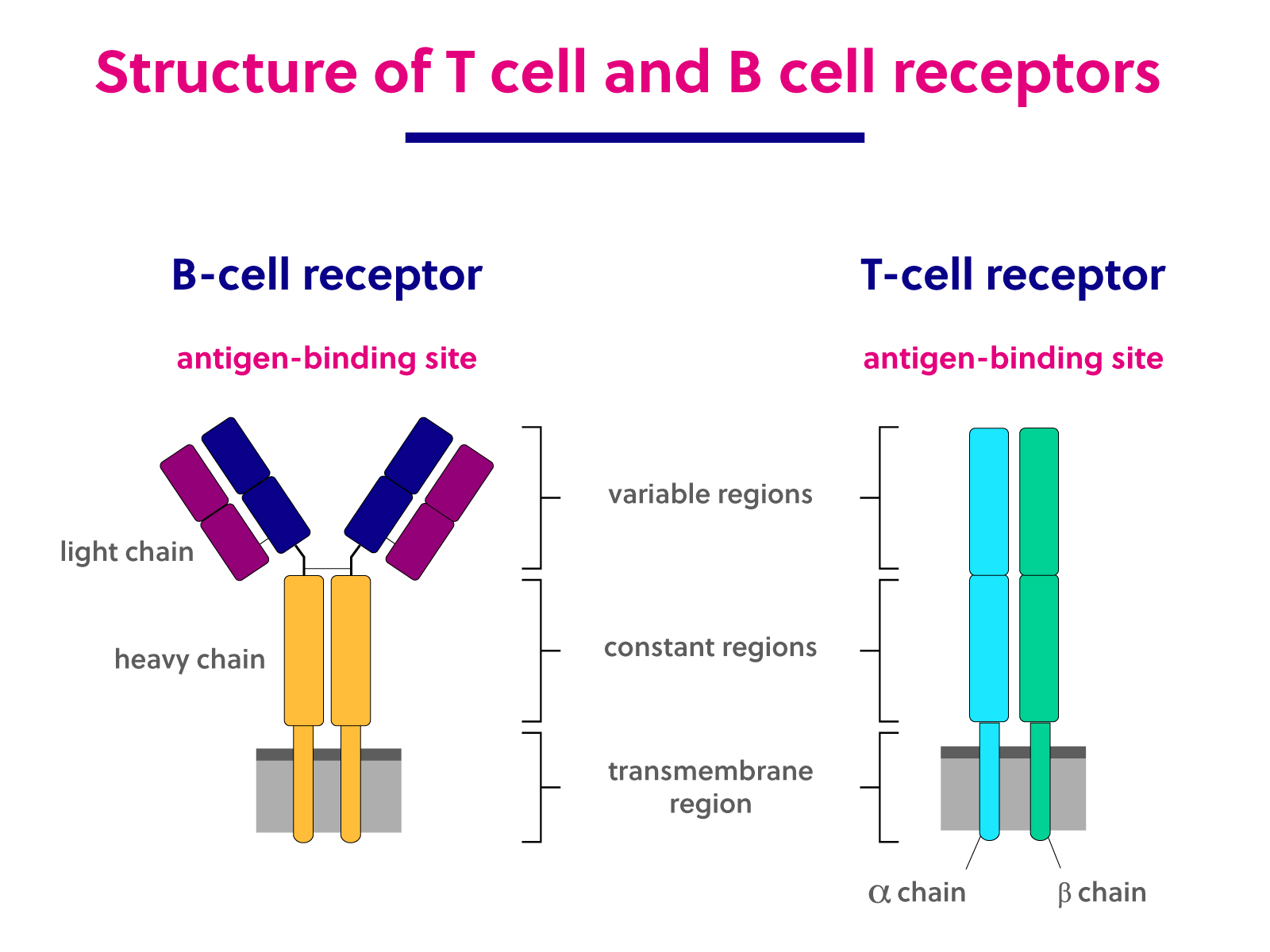
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia accounts for approximately 70% of all childhood leukemia cases (ages 0 to 19 years), making it the most common type of childhood cancer. Maturity t cells mature in the thymus. Similarities between b cells and t cells.
Epitopes are the site or region on the antigen which is recognized by the antibodies as a foreign body. The cells are nucleated and motile. Both b and t cells originate within the bone marrow.
What is the difference between t cells and b cells? Difference between t cells and b cells. Both protect the body’s immune system and help fight infections.
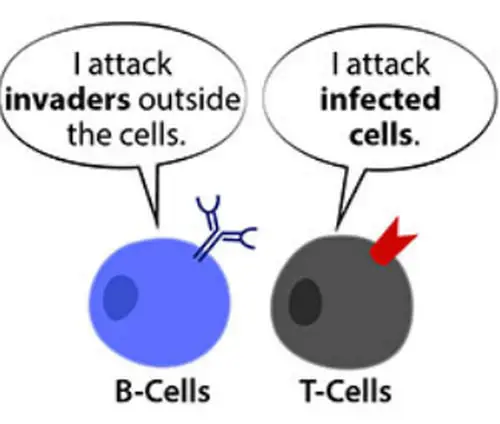
Different types of pathogens require distinct immune effector cell types to be controlled. The main difference between t cells and b cells is that t cells can only recognize viral antigens outside the infected cells whereas b cells can recognize the surface antigens of bacteria and viruses. B cells and t cells are the white blood cells of the immune system that are responsible for adaptive immune response in an organism.
T cells and b cells differ in their functions, like t cells are known to develop various immune response such as invading bacteria from body’s immune system, virus attacks, not supporting the organ transplant, etc., while b cells produce antibodies against the antigen. B cells are a type of lymphocytes that are involved in humoral immunity. Specific cd4 + t cells are important for eliciting potent b cell responses that result in antibody affinity maturation, and the levels of spike.
These cells are involved in adaptive immunity. The cytokines prime the maturation of b cells, which become plasma cells and produce antibodies to neutralise the pathogen. 272 (2008) nk cell cytotoxic t cell receptor type nk receptor (numerous activating or inhibitory) t cell receptor ligand type class i mhc, mica/b, immune.
Despite showing variance in their working, t and b cells struggle with the same aim of. B cells mature in the bone marrow while the t cells travel to the thymus and mature there. Cd8+ cytotoxic t cells, on the other hand, directly kill infected cells.
Extrafollicular cd44hicd62llopsgl1locd4+ t cells (psgl1locd4+ t cells) are associated with the pathogenesis of lupus and cgvhd, but their causal role has not been established. (9, 10) composition/proportion in the blood. Both the cells are made in the bone marrow.
In a study by gittelman et al., researchers analyzed t cell and antibody levels in 2,200 individuals from the municipality of vo, italy. T cells and b cells are white blood cells that are important cells for adaptive immunity. T cells vs b cells t cells are a type of lymphocytes that are involved in cell mediated immunity.