Pathophysiologically, acute myocardial infarction (mi) is commonly defined as a cardiomyocyte death due to a prolonged ischaemia resulting from an acute imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. St segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) an stemi is the most serious type of heart attack where there is a long interruption to the blood supply.

When there is a blockage of the coronary artery , there will be lack of oxygen supply to all three layers of cardiac muscle (transmural ischemia).
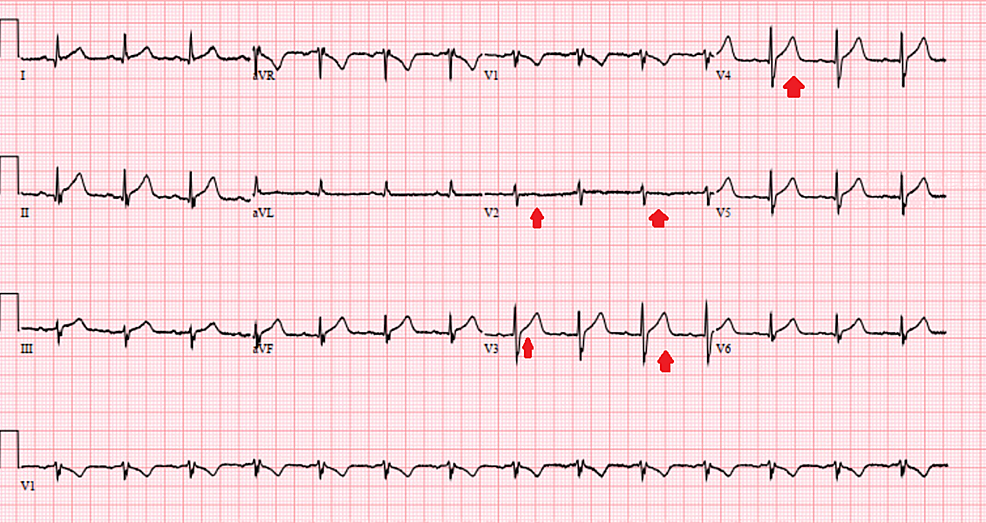
St elevation myocardial infarction. The cause of this abrupt disruption of blood flow is usually plaque rupture, erosion, fissuring or dissection of coronary arteries that results in an obstructing thrombus. For patients presenting to the emergency department with chest pain suspicious for an acute coronary. Diagnostic st elevation in absence of left ventricular hypertrophy or left bundle branch block (lbbb) 1.
Hours and day after a stemi pathological q wave: A complete thrombotic occlusion developing from an atherosclerotic plaque in an epicardial coronary vessel is the cause of stemi in the majority of cases. It usually appears as a flat line on a ecg chart.
St segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) an stemi is the most serious type of heart attack where there is a long interruption to the blood supply. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition today. 1 the ‘clinical’ definition of mi was recently updated, focusing on the values of serum markers of cardiac necrosis, such.
The “st” in st elevation myocardial infarction is the portion of the heartbeat where there should be little or no electrical activity; When a patient�s st segment is elevated, it indicates that there is electrical activity, and this in turn usually indicates that there is lack of blood flow to the heart. Summary • st segment elevation mi/stemi is a medical emergency which is the result of complete occlusion of the coronary artery causing myocardial infarction • since atherosclerotic disease is the most common cause of stemi, the pathophysiology is mainly due to the rupture of “vulnerable plaque” • clinical presentation of stemi may differ by gender and.
They should be essential in everyday clinical decision making. ≥ 1 mm (0.1 mv) in 2 other contiguous chest leads or limb leads When there is a blockage of the coronary artery , there will be lack of oxygen supply to all three layers of cardiac muscle (transmural ischemia).
New st elevation at j point ; Nstemi is the less common of the two, accounting for around 30 percent of all heart attacks. A pooled analysis of an early fibrinolytic strategy versus primary.
This is caused by a total blockage of the coronary artery, which can cause extensive damage to a large area of the heart. Pathophysiologically, acute myocardial infarction (mi) is commonly defined as a cardiomyocyte death due to a prolonged ischaemia resulting from an acute imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. Examination is variable, and findings range from normal to a critically unwell patient in cardiogenic shock.
The most important change of acute myocardial infarction, occurs within a few minutes, in the nearest leads to myocardial injury. An stemi is what most people think of when they hear the term heart attack.