Asthma / drug therapy* asthma / genetics asthma / physiopathology azithromycin / therapeutic use budesonide, formoterol fumarate drug combination / therapeutic use Continuous symptoms throughout the day, interfering with sleep and activity.
Rehabilitation and tiotropium, omalizumab, or azithromycin therapy are additional treatment options for severe asthma.
Severe persistent asthma treatment. You’ll be prescribed medication and treatment to manage the inflammation in your airways and prevent lung damage. Lung function is less than 60% of the normal level without treatment. Treatment of severe asthma focuses on trying to control the symptoms.
You’ll also be advised to reduce the risk of coming into contact with asthma triggers as much as possible, as this will reduce your risk of having a severe asthma attack. Intermittent asthma mild persistent asthma moderate persistent asthma severe persistent asthma daytime symptoms. These antibiotics work to control the number of white blood cells (neutrophils) found in your airways and reduce symptoms.
Asthma changes over time in response to triggers. • consider allergen immunotherapy by trained personnel for patients with persistent asthma when there is a clear connection between symptoms and exposure to an allergen to which the patient is sensitive. Frequent exacerbations (several times daily)
This is why it is so important to keep monitoring and managing your asthma—even when it seems to be under control. Uncontrolled asthma despite medication and lifestyle compliance or unable to taper maximal medical therapy. Basic treatment for severe persistent asthma consists of inhaled corticosteroids.
That means your level of severity can go up or down at any time. Rehabilitation and tiotropium, omalizumab, or azithromycin therapy are additional treatment options for severe asthma. Treatment of asthma includes prevention of symptoms and treatment of progressive asthma attacks.
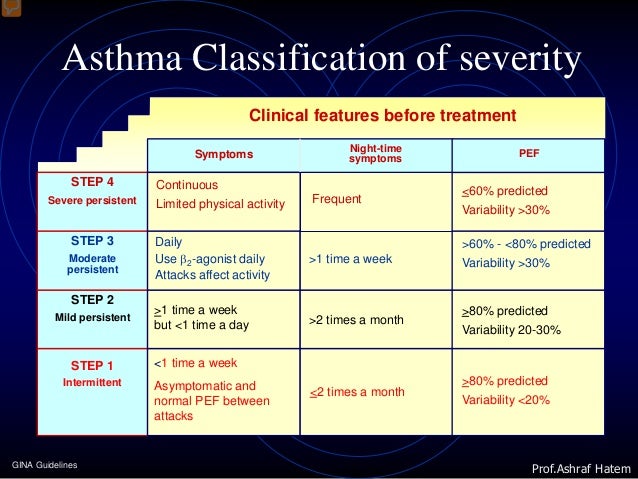
Intramuscular triamcinolone acetonide in chronic severe asthma. With severe persistent asthma, symptoms occur daily and often. There are 4 types of asthma severity:
• advise all asthma patients and all pregnant women to avoid exposure to tobacco smoke. They also frequently curtail the child’s activities or disrupt his sleep. Asthma in teens and adults.
If you or your child has persistent asthma (mild, moderate, or severe) and is receiving appropriate therapy, the goal of treatment should be to control symptoms so that they occur only as frequently as those of intermittent asthma. The basic steps in the treatment of severe asthma are confirmation of the diagnosis, treatment for comorbidities, elimination of persistent triggers, and optimization of adherence. Asthma / drug therapy* asthma / genetics asthma / physiopathology azithromycin / therapeutic use budesonide, formoterol fumarate drug combination / therapeutic use
Most people with severe asthma also benefit from albuterol nebulizer treatments. Corticosteroids inhaled corticosteroids reduce inflammation resulting in better asthma control. Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma.
[pmc free article] [google scholar] mcleod dt, capewell sj, law j, maclaren w, seaton a. Continuous symptoms throughout the day, interfering with sleep and activity. When the diagnosis of asthma is confirmed and comorbidities addressed, severe asthma is defined as asthma requires treatment with high dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a second that controller and/or systemic corticosteroids to prevent it from becoming “uncontrolled” or that
This guidance replaces ta133 and ta201. There were no asthma exacerbations after sputum induction. While there are many asthma medications like a steroid inhaler or nebulizers, your doctor will recommend the line of treatment based on your symptoms and condition.
Omalizumab is used as adjuvant therapy in patients older than 6 years with severe persistent asthma who have elevated serum ige levels and positive skin tests or in vitro reactivity to a seasonal aeroallergen when symptoms are not adequately controlled with an inhaled corticosteroid. Asthma severity is based on how often you have asthma symptoms, how often you need to use a rescue inhaler, and your risk of having an asthma attack. Because of formoterol’s rapid onset of action, the ics/laba budesonide/formoterol (symbicort) is the preferred smart regimen for patients aged 4 and over.
More details on each type of severity are below. Daily maintenance and quick relief, and simplifies asthma treatment by avoiding confusion about which inhaler to use. Individuals ages 12 years and older with persistent asthma key points • for individuals with mild
