Kuanyu l, chiachi y, chienjen h, et al. Possibly slow, halt, or even repair damage to cartilage;

1 orthopedic and arthritis center for outcomes research, division of rheumatology, inflammation and immunity, department of orthopedic surgery, brigham and women’s hospital, harvard medical school, boston,.
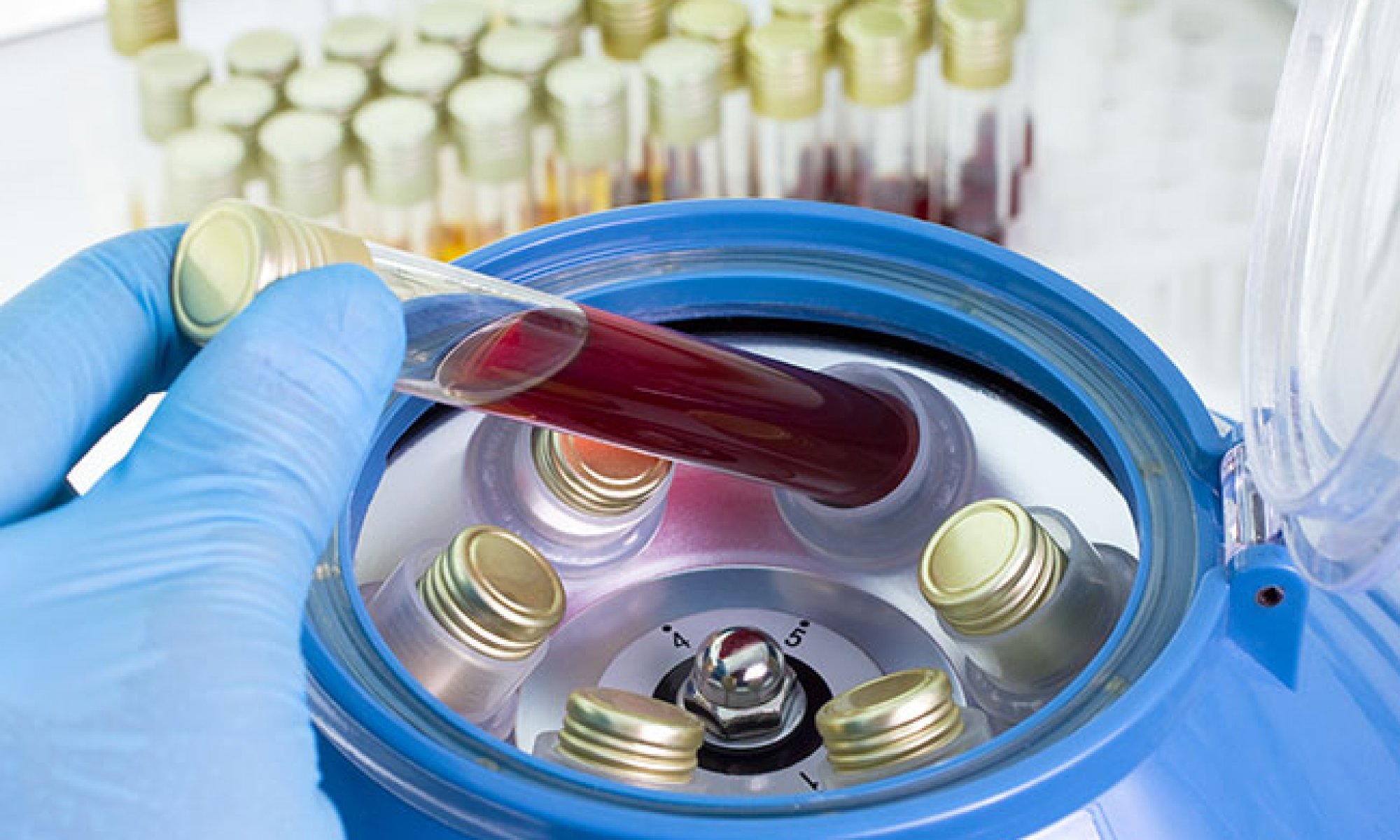
Platelet rich plasma osteoarthritis. Plasma, or the liquid portion of blood, and platelets, a type of blood cell that plays an important role in healing throughout the body. These proteins can stimulate growth in specific tissues in the body, which can be beneficial for healing. Osteoarthritis, knee, prp, platelet rich plasma.
Now a large randomized trial did not find that prp was better at improving pain or cartilage damage compared to a placebo. Platelet rich plasma (prp) is prepared from autologous blood by centrifugation to obtain a highly concentrated sample of platelets, which is four to five times higher than that of normal blood. At aoac, we do this by using a specialist filter that is small enough in size (microns) that filters out both white and red cells remaining in the prp preparation.
Prp can be formulated either white blood cell rich or white cell poor depending on the condition being treated (joint or tendon) and whether it is acute or chronic at the time of treatment. Among them, growth factors released after activation of platelets can promote cell proliferation and release extracellular matrix, which helps repair cartilage damage, and is easy. Present study is an attempt to optimise the dose and.
Kuanyu l, chiachi y, chienjen h, et al. Yurtbay a, say f, çinka h, ersoy a. Knee osteoarthritis (koa) is a common disease in aged adults.
From early degeneration to osteoarthritis arthroscopy , 27 ( 2011 ) , pp. This involves taking plasma from a small amount of the person’s own blood and injecting it into the knee. November 23, 2021 audio editors� summary 12 min 12 sec.
Platelets have granules, which release proteins called growth factors. 1 orthopedic and arthritis center for outcomes research, division of rheumatology, inflammation and immunity, department of orthopedic surgery, brigham and women’s hospital, harvard medical school, boston,. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi.
Researchers are still investigating this option. How we develop nice interventional procedures guidance The platelets undergo degranulation to release growth factors (gfs).
The injection of autologous prp into the joint space and surrounding soft tissues delivers a concentrated dose of these growth factors, which accelerate the healing process and reduce pain. A total of 23 studies were selected, with nine being controlled. When prp is injected into a joint with osteoarthritis, the growth factors have the potential to reduce inflammation and regenerate tissue.
Possibly slow, halt, or even repair damage to cartilage; Is this guidance up to date?