
The rai collects mainly in thyroid cells, where the radiation can destroy the thyroid gland and any other thyroid cells. 128x128 matrix, 50 seconds per stop, 64 stops.
The rai collects mainly in thyroid cells, where the radiation can destroy the thyroid gland and any other thyroid cells.
I 131 ablation therapy. Subjects� characteristic such as tumor type, tumor size, and nodal metastasis at the time of surgery were noted. Radioactive iodine (radioiodine) therapy for thyroid cancer. Uptake in identified regions or lesions should be quantitated
Benign thyroid conditions (obstructive goiter, etc.) contraindications 1. The original histology/ pathology report must be obtained, together with the surgeon�s operative report to assess the risk category (low, moderate, high) of the patient. The rai collects mainly in thyroid cells, where the radiation can destroy the thyroid gland and any other thyroid cells.
B) 13 i therapy has been used to treat residual thyroid cancer and metastatic disease after partial or complete thyroidectomy. The aim of therapy is to treat hyperthyroidism by destroying sufficient thyroid tissue to render the patient either euthyroid or hypothyroid. Doctors use it to treat an overactive thyroid, a condition called hyperthyroidism.
Radioiodine therapy for hyperthyroidism is performed as an outpatient procedure. Based on the primary goal of the rait, there are two main forms of the procedure. Hyperthyroidism can be caused by graves� disease, in which the entire thyroid gland is overactive, or by nodules within the gland which are locally.
It concentrates in the thyroid gland and begins to destroying the gland. Used to reduce thyroid function for hyperthyroid patients typical administered doses are: Common indications for therapy of thyroid diseases with 131 i include, but are not limited to, benign diseases such as certain types of hyperthyroidism (131 i may be indicated for the treatment of graves disease and toxic nodular [uninodular or multinodular] disease ) and nontoxic nodular goiter (131 i therapy may be used successfully to diminish the size of.
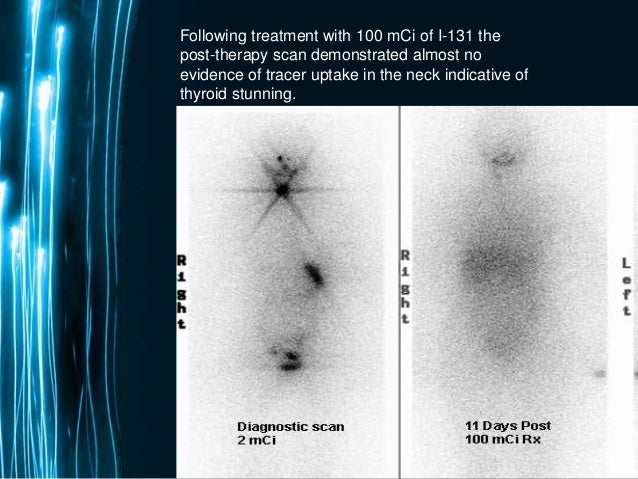
Once it is swallowed, it goes to the gastrointestinal tract and gets absorbed into the bloodstream. Your thyroid gland absorbs nearly all of the iodine in your body. The efficacy of ablation therapy with a dose of 100 mci was 85, 7%, significantly better than 57% with a dose of 80 mci dose (p=0, 04).
Review all images with the nuclear medicine physician on duty before releasing the patient. Center the sternal notch in the fov. Treatment options include medication (ptu), surgery and i131 ablation.
128x128 matrix, 50 seconds per stop, 64 stops. The recurrence rate for patients with metastases was 56% and those without metastases was 25%. However, the level of thyroid autoantibodies will decrease after the treatment;
Thyroid remnant ablation after total thyroidectomy is a generally accepted therapy for patients with thyroid cancer. A) 1311 therapy has been used for postoperative ablation of thyroid remnants after th~roidectomy. Before this treatment, i should have as little to eat as possible for at least four (4) hours, preferably since midnight.
Graves often treated medically first, but often medication compliance is poor due to side effects.