It does not cover ventilator‑associated pneumonia. Treatment length is typically 7 days.

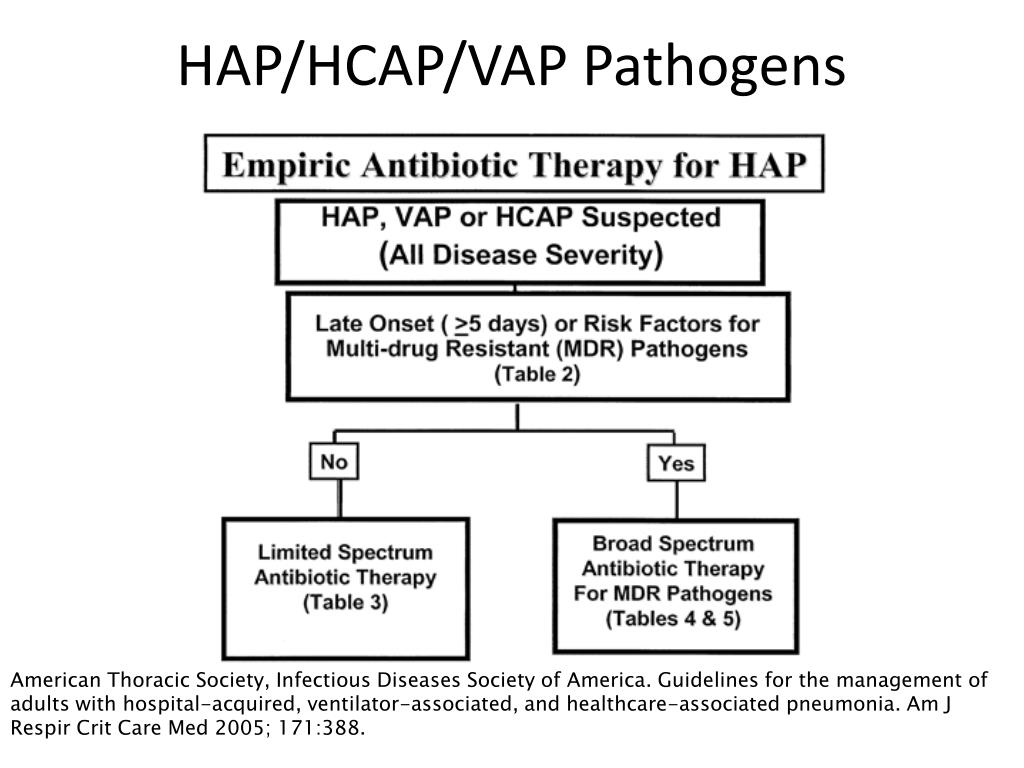
Be aware of local hap pathogen distribution and resistance patterns.
Hospital acquired pneumonia treatment. Maintain oxygen spo 2 > 92% (if at risk for hypercapnia then spo 2 > 88%). It aims to optimise antibiotic use and reduce antibiotic resistance. Risk factors, microbiology, and treatment.
It does not cover ventilator‑associated pneumonia. To help with diagnosis, the updated guideline recommends that cultures of respiratory secretions and blood should be obtained for all patients with suspected hap/vap. Be aware of local hap pathogen distribution and resistance patterns.
Download our actionable patient safety solutions as a first step and join the movement! The main reason was the. Pneumonia complicates hospitalization in 0.5 to 2.0% of patients and is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality.
Consider urinary antigen testing for pneumoniae. Major differences compared to previous 2005 guidelines were: Treatment length is typically 7 days.
Uncomplicated pneumonia treatment in the outpatient setting usually should last 5 to 10 days.54 inpatient admission for pneumonia warrants longer duration of antibiotic therapy, typically 7 to 10 days of combined parenteral and oral therapy or at least 1 week after becoming afebrile.58 complicated cases of pneumonia will require a minimum of 2 weeks of therapy. People who are seriously ill may be placed in an intensive care unit and sometimes put on a ventilator mechanical ventilation mechanical ventilation is use of a machine to aid the movement of air. This review compares hap and vap, highlighting differences in natural history, risk factors, and bacteriology that necessitate a different approach to the therapy of hap, compared with vap.
This guideline sets out an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for hospital‑acquired pneumonia. Ad · 4700+ international hospitals have taken the pledge to end preventable pneumonia. However, considering the resistance pattern of the isolated pathogens, both classifications demonstrated a rather lower treatment adequacy;
In general, patients developing pneumonia (as defined in therapeutic guidelines, antibiotic) after 48 hours of admission qualify as hospital acquired (nosocomial) infections.