New cdc recommendations advise universal hepatitis b vaccination for adults aged 19 to 59. What needle size should be used?
New cdc recommendations advise universal hepatitis b vaccination for adults aged 19 to 59.
Hep b vaccine recommendations. • documentation of immunity does not require further action even if the individual is exposed. Centers for disease control and prevention (cdc). Vaccine recommendations on hepatitis b hepatitis b vaccination of infants, children, and adolescents (acip recommendations) healthcare personnel vaccination recommendations pdf icon [1 page] external icon
More than 2 million people in the united states have chronic hepatitis b. Hepatitis b is vaccine preventable. Hepatitis b immunization recommendations for premature infants footnote 1 weighing less than 2,000 grams, by maternal hepatitis b surface antigen (hbsag) status maternal hbsag status recommendation
At what anatomic site should hepatitis b vaccine be administered to adults? • pvst should be completed 1 to 2 months after completion of the third dose. The gluteus muscle should not be used as a site for administering hepatitis b vaccine.
Dynavax has donated 10,000 doses of its hepatitis b. Or b) the individual did not develop immunity against The first hepatitis b vaccine to become available commercially in 1982 consisted of hbsag purified from the plasma of persons with chronic hbv infection.
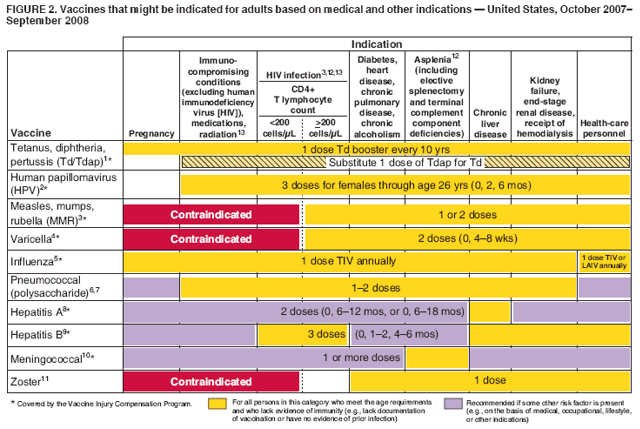
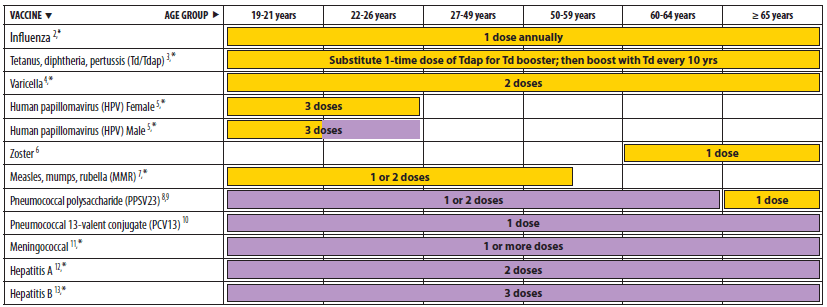
New cdc recommendations advise universal hepatitis b vaccination for adults aged 19 to 59. The hepatitis b vaccine is recommended for all infants and children up to age 18 years by the world health organization (who) and the u.s. *infants whose mothers are hbsag+ or whose hbsag status is unknown should receive the third dose at 6 months of age +an additional dose at 4 months is acceptable if the clinician prefers to use a combination vaccine that contains hepatitis b vaccine
Hcp who perform tasks that may involve exposure to blood or body fluids should be tested for hepatitis b surface Completing the hepatitis b vaccine. The average incubation period for hepatitis b is 40 to 160 days.
The advisory committee on immunization practices (acip) recommends vaccination of adults at risk for hbv infection, including universal vaccination of adults in settings in which a high proportion have risk factors for hbv infection and vaccination of adults requesting protection from hbv without acknowledgment of a specific risk factor. Hospitals, gp surgeries and sexual health or gum clinics usually provide the hepatitis b vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection. A woman found to be hbsag positive should be monitored carefully to ensure that the infant receives hbig and begins the hepatitis b vaccine series no later than 12 hours after birth and that the infant completes the recommended hepatitis b vaccine series on schedule.” 7.
Hepatitis b vaccine on the nhs. A) the antibody level has waned to less than 10 iu/l, but the individual is still immune to the hepatitis b virus. Four doses at 0, 1, 2, and 6 months are usually recommended.
What needle size should be used? I) administer hepatitis b vaccination ii) if an individual had hepatitis b vaccinations before either : For the second series, a different brand of vaccine should be administered.
The acip specifically recommends that adults aged 19 to 59 and those 60 years and older with risk factors for infection “should” receive the hepatitis b vaccine, and it further stipulates that. The regional coverage rate with three doses of hepatitis b vaccine (hepb3) was 76% in 2008, according to data reported to who, compared with 67% in 2003 and 40% in 2000. Current hepatitis b vaccine recommendations.
Hepatitis b is spread when blood, semen, or other body fluids from a person infected with the virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. Without proper treatment, one in four of these individuals will die from liver failure or cancer. This indicator uses the total regional population of children under 1 year of age as a denominator and includes children in countries without universal immunization programmes.
The cdc recommends universal hepatitis b vaccination within 24 hours of birth for medically stable infants greater than 2000 grams, has removed permissive language that allowed the vaccine to be delayed until after hospital discharge, and continues to recommend hepatitis b vaccination and hepatitis immune globulin regardless of birth weight within 12 hours of birth. Hepatitis b vaccine should be offered to people with hiv who are at risk of infection, as they are more likely to contract hepatitis b and also to develop chronic infection. If an unadjuvanted vaccine is being used (engerix®, hbvaxpro®) a high dose (40 µg) is recommended.