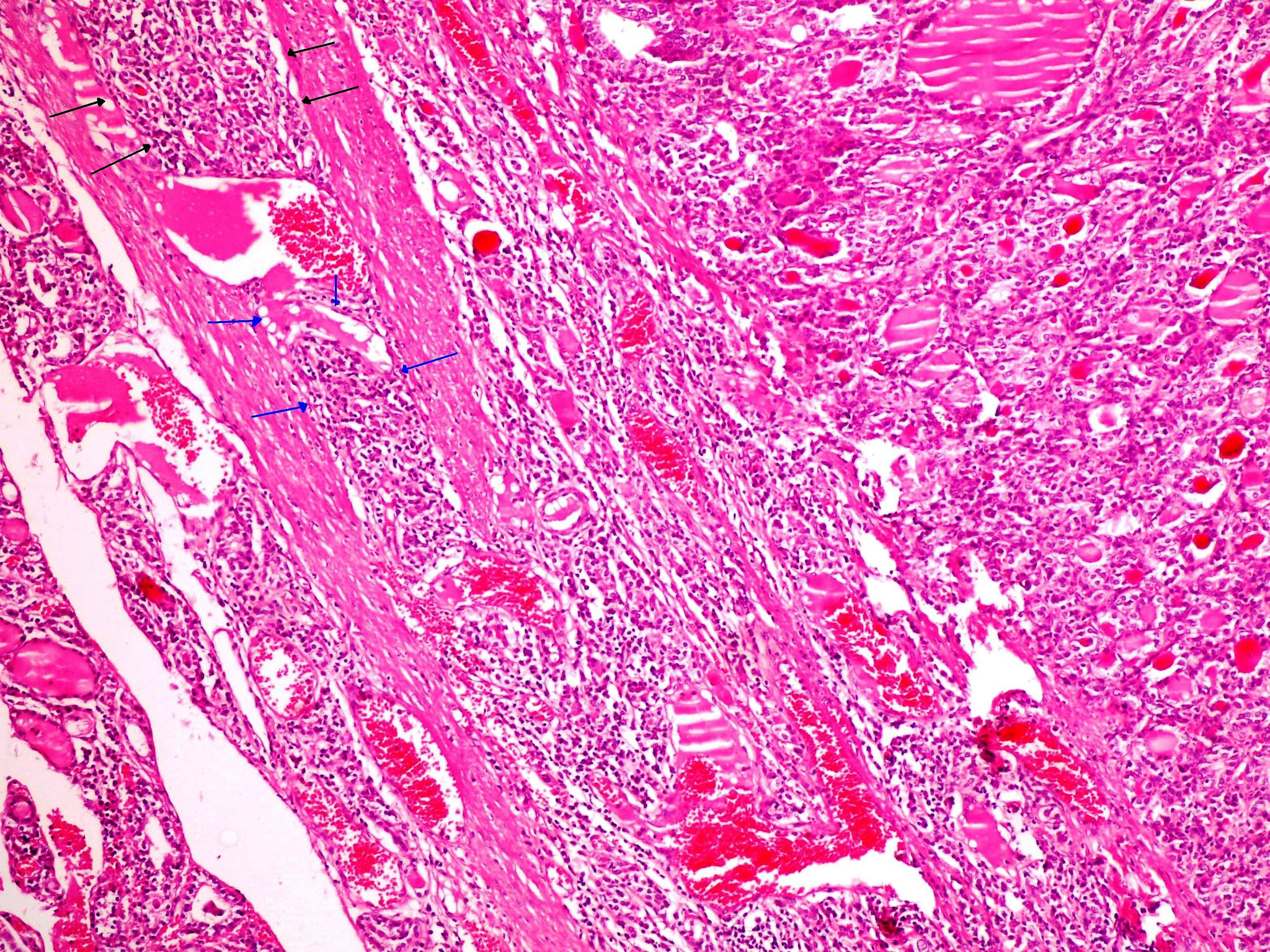
Hematogenous spread, as in this case, is however much more common with 20% or so of patients having distant hematogenous metastases at presentation. Hematogenous spread, as in this case, is however much more common with 20% or so of patients having distant hematogenous metastases at presentation.
The tumour cells in follicular carcinoma look similar to the cells in a follicular adenoma.
Follicular carcinoma of thyroid. In the respective chapter of the who classification of tumours of endocrine organs, follicular thyroid carcinoma (ftc) is defined. The right lobe of the thyroid was sectioned and reveals a large solid nodule with necrotic and hemorrhagic areas. It usually affects people under 40, particularly women;
We encourage you to print out these guidelines for your reference. Epidemiology it typically occurs in women and in an older age group than pa. Usually solitary cold nodule on radionuclide scan.
Follicular carcinomas are rare thyroid malignancies that are difficult to diagnose preoperatively. Follicular thyroid carcinoma, abbreviated ftc, is an uncommon malignancy of the thyroid gland. The most important difference is that in follicular carcinoma, the.
Follicular carcinoma is a primary malignancy neoplasm of the follicular cells in the thyroid gland. Hematogenous spread, as in this case, is however much more common with 20% or so of patients having distant hematogenous metastases at presentation. It is a kind of tumor (abnormal growth) found in your thyroid gland.
Insufficient dietary iodine is a risk factor. Fine needle aspiration is an excellent diagnostic tool and should be the initial step in managing the solitary thyroid nodule. Follicular thyroid carcinoma (ftc) is the second most common thyroid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma.
For more details about the management of differentiated thyroid cancer (papillary, follicular, and variants), visit these sections of our web site. Precursor of thyroid hormones ; It is also known as follicular carcinoma.
Follicular thyroid carcinoma (ftc) is the second most common thyroid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma. Hindawi�s academic journals cover a wide range of disciplines. Follicular thyroid carcinoma is diagnosed based on pathologic confirmation of follicular cells that do not have the nuclear atypia seen in papillary thyroid cancer including capsular and vascular invasion.
Follicular ca is the second most common malignancy of the thyroid gland. Most tumours are at least partially separated from the normal thyroid gland by a thin barrier called a capsule. This review will discuss the reasons underlying such an observation focusing on the evolution of the morphological and immunohistochemical diagnostic criteria of follicular thyroid tumors.
Produced exclusively by the thyroid gland [14] indicated after total thyroidectomy or. The authors studied the clinical course of 132 patients with ftc to determine whether there was a direct relation between the histologic degree of invasion, tumor recurrence, and patient survival. Thyroid follicular carcinoma is a type of malignant neoplasm of the thyroid gland and is derived from the thyroid follicular epithelial cell.
Follicular thyroid carcinoma is also called ftc. The authors studied the clinical course of 132 patients with ftc to determine whether there was a direct relation between the histologic degree of invasion, tumor recurrence, and patient survival. These cells make thyroid hormones (special chemicals) that control how.
Follicular or papillary thyroid cancer thyroglobulin ( tg ) : The tumor comes from a part of the thyroid gland called follicular cells. A follicular adenoma is a benign.
The thyroid cancer specialists who developed the guidelines include many thyca medical advisors and conference and workshop speakers. Follicular adenoma and follicular carcinoma of the thyroid gland are tumors of follicular cell differentiation that consist of a microfollicular architecture with follicles lined by cuboidal epithelial cells. Follicular carcinomas are often associated with repeated bouts of iodine deficiency resulting in nodular endemic goiters.
There are 4 main types of thyroid cancer: The tumour cells in follicular carcinoma look similar to the cells in a follicular adenoma. Follicular carcinoma cannot be diagnosed with certainty by cytologic features alone;
The diagnosis rests on the histologic findings of blood vessel or tumor capsule.