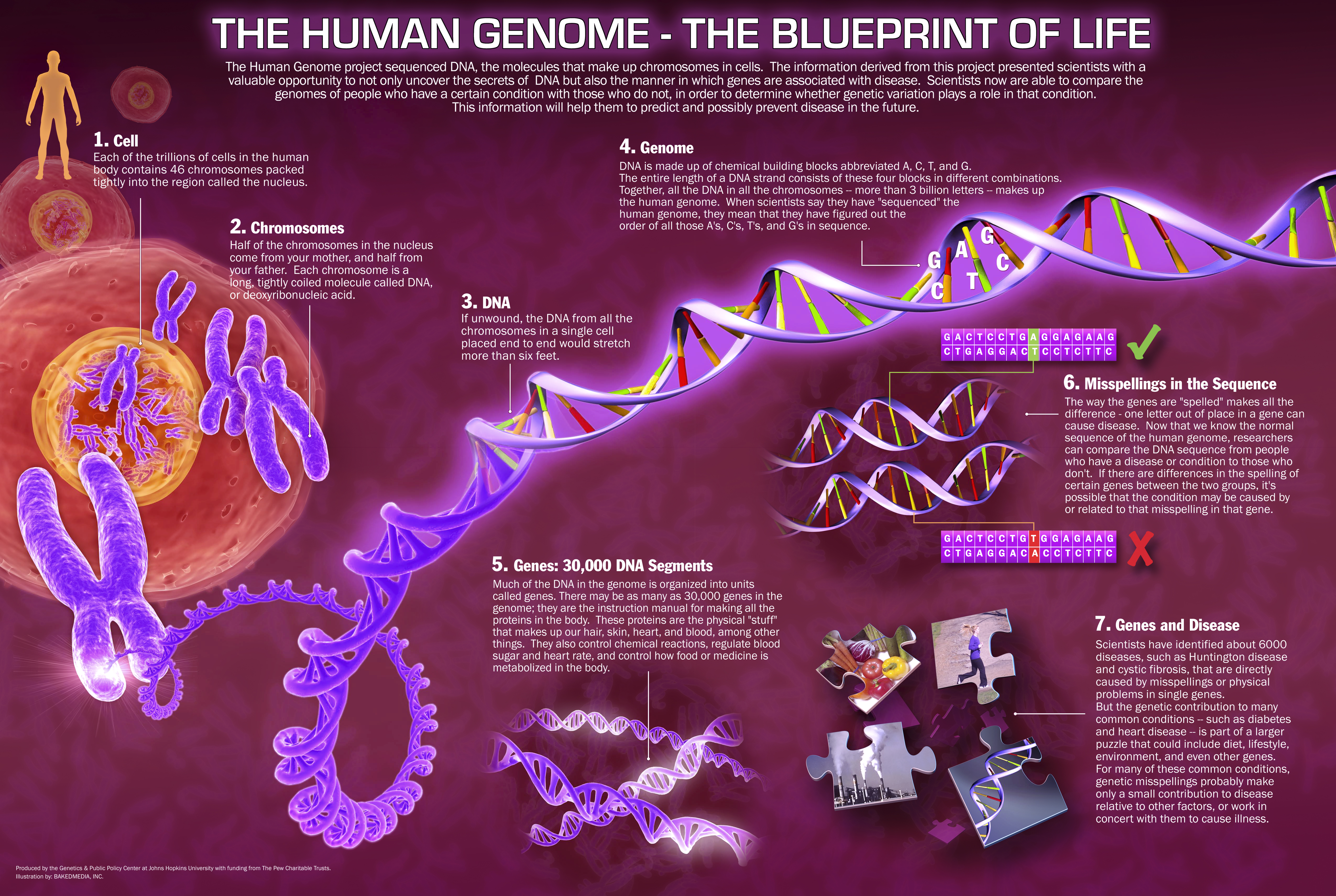
The human genome, like the genomes of all other living animals, is a collection of long polymers of dna. The sequencing of the first human genome cost over $3 billion ,.
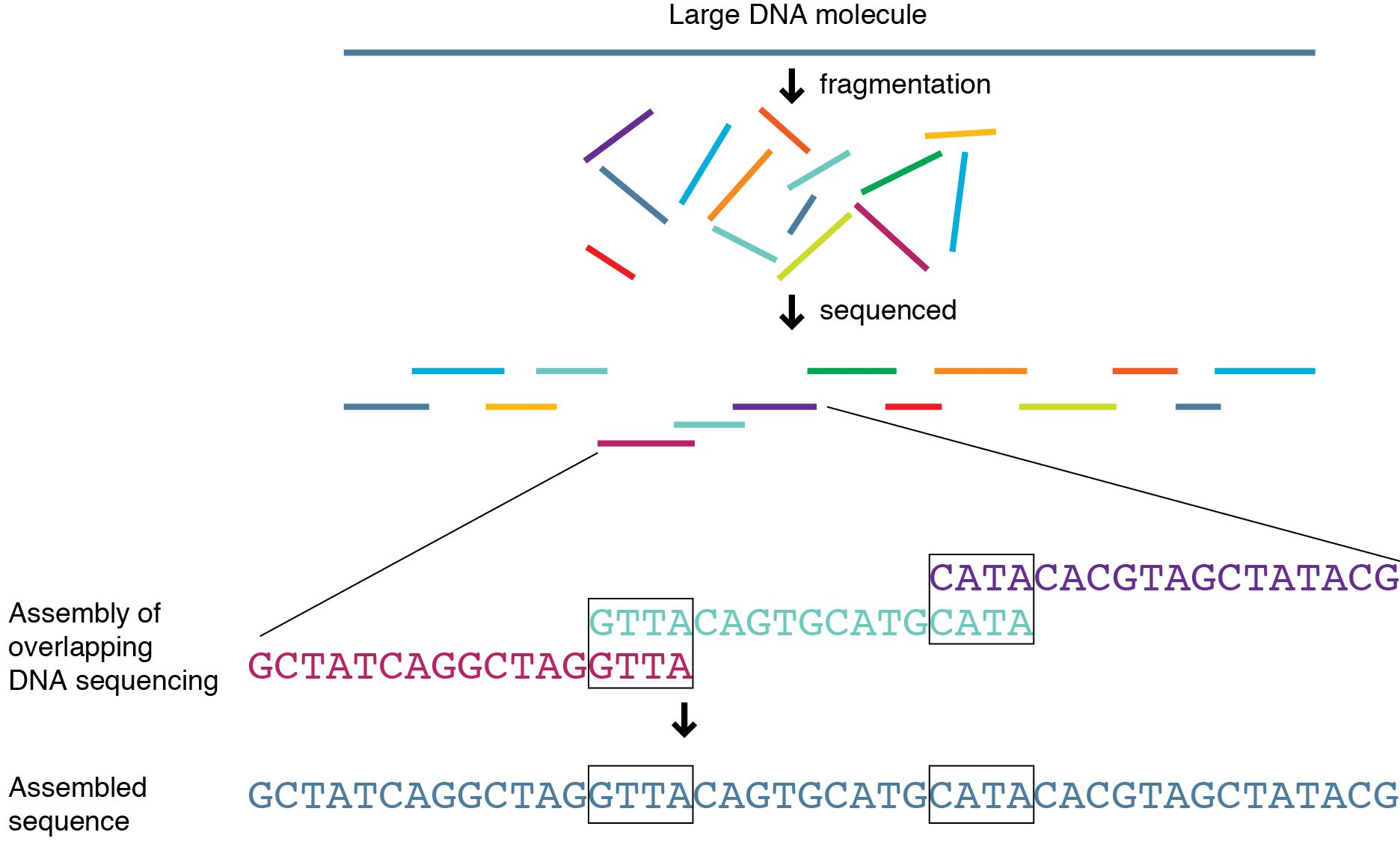
• most fragment assembly algorithms include the following 3 steps:
Entire human genome sequence. Screener, overlapper, unitigger, scaffolder, and repeat resolver, respectively. This includes a big portion of the missing 8 percent from the first “draft” of the genome. Human genome project results in 2003, an accurate and complete human genome sequence was finished two years ahead of schedule and at a cost less than the original estimated budget.
The human genome, like the genomes of all other living animals, is a collection of long polymers of dna. Wgs has the ability to evaluate every base in the genome and navigate the complexity of genomic variants that make us unique. A n international team of scientists says it has sequenced and assembled the entirety of the human genome, including parts that were missed in the sequencing of the first human genome two decades ago.
The wga assembler consists of a pipeline composed of five principal stages: The complete sequence of a human genome sergey nurk 1,* , sergey koren 1,* , arang rhie 1,* , mikkorautiainen 1,* , andrey v. The human genome project was the international research effort to determine the dna sequence of the entire human genome.
The human genome is stored in 46 different strings (chromosome), and these strings have no natural order. Dna sequence information underpins genetic research, enabling discoveries of important biological or medical benefit. Each organism has a unique dna sequence which is composed of bases (a, t, c, and g).
Vollger 4 , nicolas altemose 5 , lev uralsky 6,7 ,ariel gershman 8 , sergey aganezov 9 , savannah j. Rapidly dropping sequencing costs and the ability to produce large volumes of data with. The genome, or genetic material, of an organism (bacteria, virus, potato, human) is made up of dna.
Bzikadze 2 , alla mikheenko 3 , mitchell r. When we talk about “sequencing” the genome, we mean writing out the dna bases (c, g, t, and a) in the order they appear in most people. Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders, characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, and tracking disease outbreaks.
Human whole genome sequencing (hwgs) enables researchers to describe the full genetic composition of individuals and characterize entire human genomes. Scientists say they have finally sequenced the full human genome. These polymers are maintained in duplicate copy in the form of chromosomes in every human cell and encode in their sequence of constituent bases (guanine [g], adenine [a], thymine [t], and cytosine [c]) the details of the molecular and physical characteristics that form the.
Researchers generate complete human x chromosome sequence jul 14, 2020 landmark study details sequencing of 64 full human genomes to better capture genetic diversity If you know the sequence of the bases in an organism, you have identified its unique dna fingerprint, or pattern. Whole genome sequencing increases diagnosis of rare disorders by nearly a third.
The human genome is written in dna, and while your exact genome is unique to you, about 99.9% of it is identical across all people. This sequence can then serve as a reference guide for research into human biology, evolution,. What is whole genome sequencing (wgs)?
The numbers used to refer to the genomes are based on their order when arranged by size. • usually we know with some approximation the length of the target sequence. All operations on the genome (such as copying it before mitosis) happen in parallel, with proteins operating on each chromosome individually.
Whole genome sequencing (wgs) decodes all 6.4 billion dna base pairs in the human genome including the complete set of all 20,000 genes, mitochondrial dna, and the y chromosome. • most fragment assembly algorithms include the following 3 steps: Whole genome sequencing from a single blood test picks up 31% more cases of rare genetic disorders than standard.
The sequencing of the first human genome cost over $3 billion ,.