From the origins of memory t cells omilusik and goldrath, 2017 two proposed models for memory t cell formation: The body doesn�t just produce one type of antibody either;
Pepper states that during the contraction phase of the body’s immune response, the body produces roughly 10% more immune cells, specifically b and t cells.
Do t cells produce antibodies. The helper t cell stimulates b cells through the release of cytokines. B cells and t cells. 2017, where gene methylation patterns in naïve, effector and memory t cells were analyzed, supported that.
While there may not be as many b cells over time, they retain the memory of producing antibodies so they can make them quickly when needed. The cytokines prime the maturation of b cells, which become plasma cells and produce antibodies to neutralise the pathogen. They help to shape, activate and regulate the adaptive immune response.
Helper t cells are important regulators of immune responses to specific antigens. The stimulated b cell undergoes repeated cell divisions, enlargement and differentiation to form a clone of. T cells are formed in the bone marrow but they only fully develop in the thymus gland.
Follicular helper t cells (tfh). Since t cells don�t target specific areas on the surface of viruses the way antibodies do, they tend to be less affected when a pathogen undergoes mutations, redd said. Memory t cells arise from naïve t cells or b.
Some helper t cells, called th1 cells, can activate cd8 t cells, and other helper t cells, called th2 cells, can. They help to shape, activate and regulate the adaptive immune response. Both t cells and antibodies work together often in the immune system to destroy or disable pathogenic microbes like harmful bacteria and viruses.
Cd8+ cytotoxic t cells, on the other hand, directly kill infected cells. Alongside antibodies, t cells are a key player in the immune response against pathogens. These cells were discovered just over a decade ago as germinal center t cells that help b cells to produce antibodies.
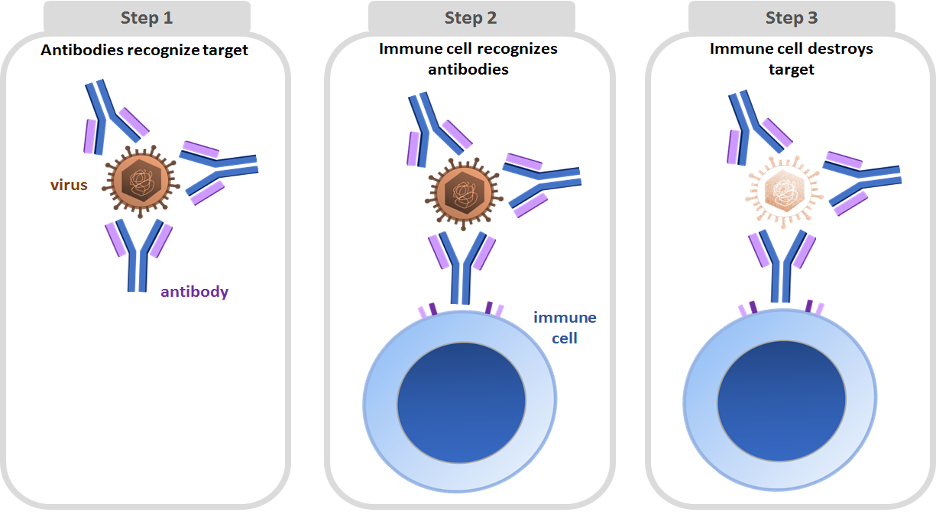
Natural flora, physical barriers, chemical barriers, phagocytes, histamine, inflammation, fever,. The antibodies bind to viruses and neutralise them, preventing them from infecting cells. What is the role of t cells and antibodies in immunity?
They stimulate plasma b cells to produce antibodies. The body doesn�t just produce one type of antibody either; “antibodies alone can protect, including at relatively low levels, but t cells are also helpful if antibody levels are insufficient,” barouch says.
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system. When a t lymphocyte sees the same peptide on the macrophage and on the b cell, the t cell stimulates the b cell to turn on antibody production. Another type of t cell kills cells.
B cells develop into plasma cells that produce antibodies (t cells do not); There are two main types of lymphocytes: 2017 and youngblood et al.
Each locks onto different parts of an invader. Summary of t cells vs. Like b cells, which produce antibodies, t cells are central players in the immune response to viral infection [1].
Pepper states that during the contraction phase of the body’s immune response, the body produces roughly 10% more immune cells, specifically b and t cells. T cells are another type of white blood cell that work alongside b cells to fight infections. T cells and antibodies are related in that certain t cells trigger the release of antibodies from b cells.
To do this they need to tell the difference between the infected cells and healthy cells with the help of special molecules called antigens. Cd4+ t cell functions include activating other immune cells, releasing cytokines, and helping b cells to produce antibodies. The t cell immune response is much more difficult to.
It produces a messy, chaotic zoo of them. The b cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins. Findings by akondy et al.
Why immunity is about more than antibodies. Sometimes individuals with a very vigorous t cell immune response will be protected from a pathogen even though they produce low amounts of antibody. The t cells destroy the body�s own cells that have themselves been taken over by viruses or become cancerous.
Antibodies initially produced by the body after infection had started to drop during this period. From the origins of memory t cells omilusik and goldrath, 2017 two proposed models for memory t cell formation: Like b cells, which produce antibodies, t cells are central players in the immune response to viral infection.