It is called dlbcl because: It is a cancer of b cells.

It is the most common subtype of lymphoma, accounting for around 30% of all lymphoma cases and affects around 2,000 australians each year.
Diffuse large b cell non hodgkins lymphoma. B cells transform through many stages to become cells that are able to fight disease. Read part 2 to learn about the tests of cells that are used to confirm (diagnose) dlbcl. The nccn recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment.
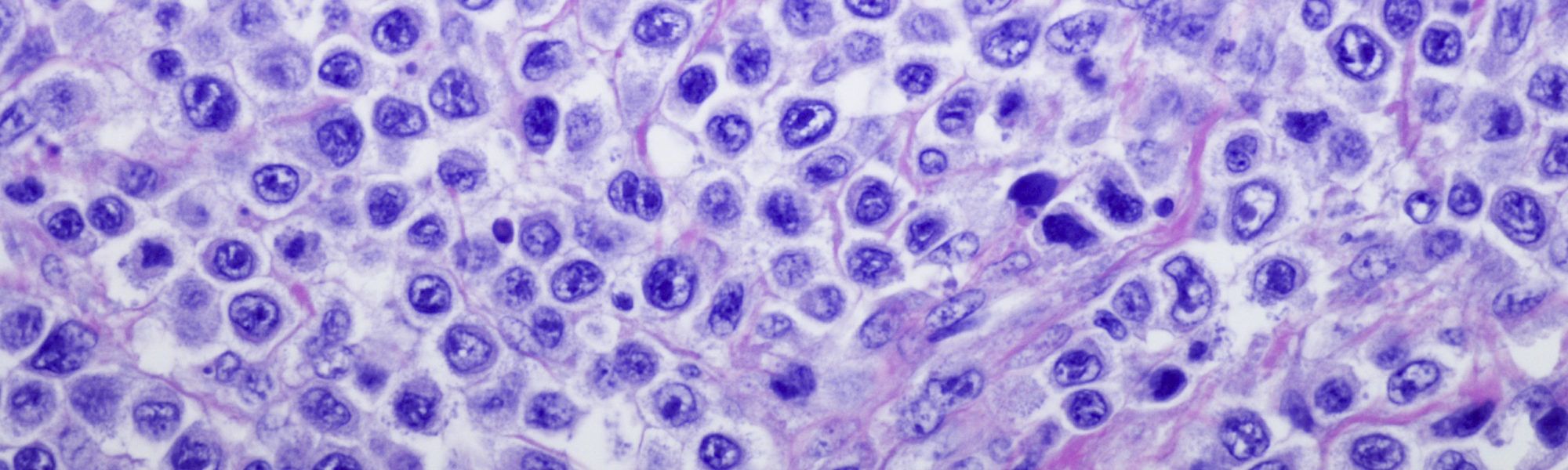
It develops from abnormal b cells. Nhl is a cancer of the lymphatic system. Under the microscope, large malignant lymphocytes are seen diffusely throughout the specimen.
It develops when the body makes abnormal b lymphocytes. The lymphoma cells are also scattered throughout the lymph nodes or tissue. The abnormal cells are larger than normal, healthy b cells.
These lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that normally help to fight infections. Most often, the treatment is chemotherapy (chemo), usually with a regimen of 4 drugs known as chop (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), plus the monoclonal antibody rituximab (rituxan). When looked at under a microscope, the lymphoma cells look very large compared to normal lymphocytes.
She describes undergoing chemo, being an aya (adolescent young adult) cancer patient, how to ask for help, and the support that made the most impact. Though aggressive, it does respond well to chemotherapy. Men are more frequently affected than women [1].
Dlbcl can occur at any age, but most people are diagnosed when they are in. When you have a lymphoma, the abnormal lymphocytes build up in lymph nodes or. It is a cancer of b cells.
Dlbcl is a cancer of mature b cells from the lymph system. It is called dlbcl because: It is the most common subtype of lymphoma, accounting for around 30% of all lymphoma cases and affects around 2,000 australians each year.
The lymphoma cells look fairly large when seen with a microscope. She takes us through her journey: It grows quickly in the lymph nodes and often the spleen, liver, bone marrow, or other organs are also affected.
From the fear of navigating it alone to the “scanxiety,” the physical and mental side effects, to survivorship. All patients had disease of the dlbcl subtype and those patients had primary. More than 18,000 people are diagnosed with dlbcl each year.
This disease presents as a rapidly growing mass or enlarging lymph nodes in a nodal or extranodal site.