The lymph system lymphoma is a cancer of the lymph (or lymphatic) system. Nodularity is present, at least focally, in approximately 30% of cases of mantle cell lymphoma at the time of initial diagnosis.

There are two main types, one that impacts mostly the skin, known as cutaneous alcl.
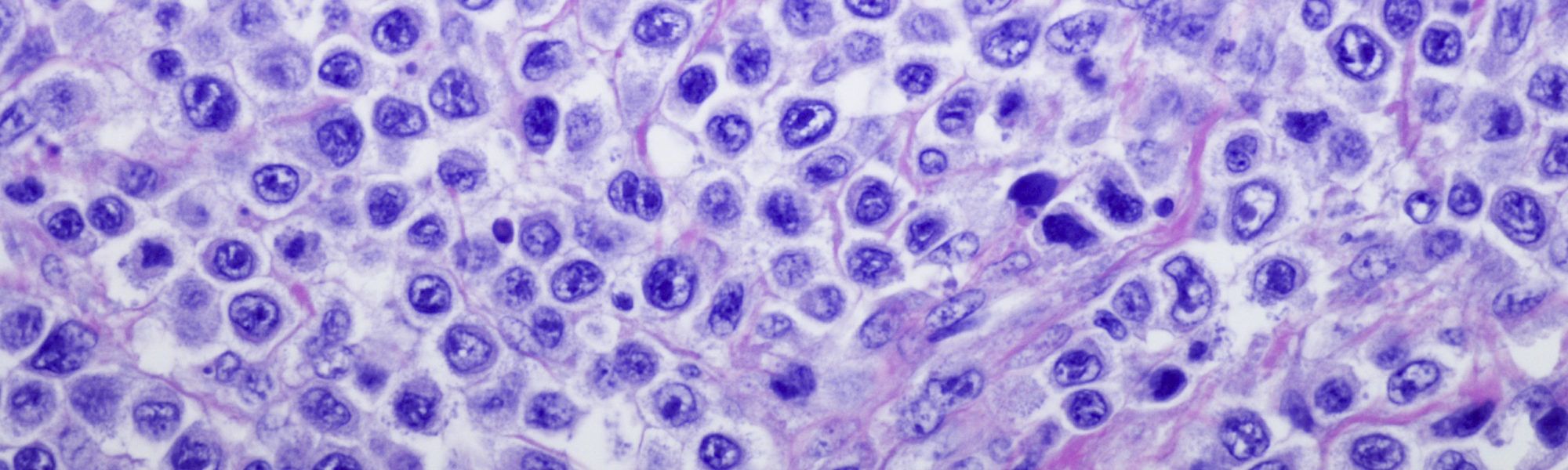
Diffuse large b cell non hodgkin lymphoma. Under the microscope, large malignant lymphocytes are seen diffusely throughout the specimen. There are two main types, one that impacts mostly the skin, known as cutaneous alcl. The lymphoma cells are also scattered throughout the lymph nodes or tissue.
It is the most common subtype of lymphoma, accounting for around 30% of all lymphoma cases and affects around 2,000 australians each year. It can start in the lymph nodes or outside of the lymphatic. Diffuse large b cell lymphoma.
Generally for people with dlbcl: The lymph system lymphoma is a cancer of the lymph (or lymphatic) system. Treatment of localized and advanced disease varies considerably.
It develops when the body makes abnormal b lymphocytes. When looked at under a microscope, the lymphoma cells look very large compared to normal lymphocytes. Nodularity is present, at least focally, in approximately 30% of cases of mantle cell lymphoma at the time of initial diagnosis.
It develops from abnormal b cells. This has prompted the analysis of another series of patients with primary intestinal dlcl to depict the clinical features and the outcome of that disease and to compare those with that for pg involvement. These are types of lymphoma that affect b lymphocytes.
It is clinically, morphologically and genetically a heterogeneous group of tumors composed of. Dlbcl can occur at any age, but most people are diagnosed when they are in. Nhl is a cancer of the lymphatic system.
Diffuse large b cell lymphoma (dlbcl) is the most common type of high grade lymphoma. These lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that normally help to fight infections. The nccn recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment.
It is called dlbcl because: Most often, the treatment is chemotherapy (chemo), usually with a regimen of 4 drugs known as chop (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), plus the monoclonal antibody rituximab (rituxan). 60 in 100 people (60%) will.
Risk stratification with the international prognostic index (ipi) score is also provided. The abnormal cells are larger than normal, healthy b cells.