For patients who are unsuitable for or who decline anticoagulants, asa 81 mg daily is suggested. Recommend antithrombotic therapy with oral anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy but preferably oral anticoagulation.

Score (chads 2), which showed incongruence between scores with a critical tm in the tee.
Chads vasc score anticoagulation. Score (chads 2), which showed incongruence between scores with a critical tm in the tee. Therapeutic decisions need to balance the individual benefit of reducing thromboembolic risk against the potential harm due to an increase in bleeding risk in this. Olesen et al thromb haemost.
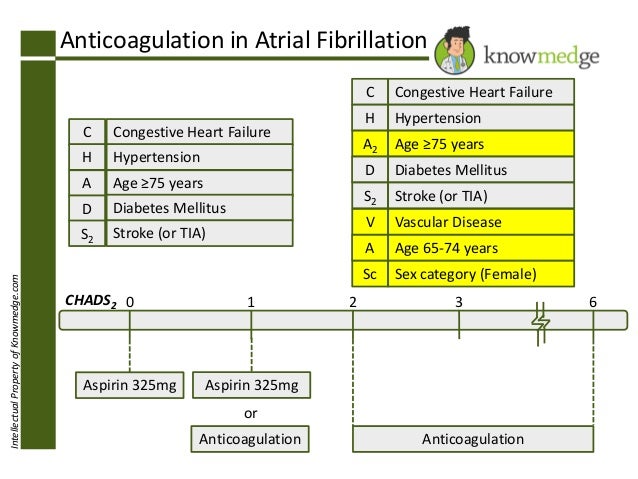
Management of anticoagulation for indications such as venous thromboembolism and mechanical heart valves. A high score is the same as a higher stroke risk, and a low score means the lower stroke risk. Over 65 years all increasing the risk of both stroke and major bleeding.
Recommend antithrombotic therapy with oral anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy but preferably oral anticoagulation. In patients with a chads. The result from chads2 is simple, validated by numerous studies.
Anticoagulation may be with apixaban, dabigatran etexilate, rivaroxaban or a vitamin k antagonist. Thus, this study is only evaluating changes in anticoagulation recommendations and does not address the. Before the introduction of both the chads 2 and cha 2 ds 2 vasc scores, the anticoagulation and risk factors in af (atria) cohort was established.
This will be true especially for women, younger patients, and those with a. 32,33 this score encompasses a. Take the bleeding risk into account.
Chads 2 score 5 or 6. In situations where both the perceived bleeding risk and stroke. The chads(2) score classified 33% as requiring oral anticoagulation.
In spite of a mean age of 49 years,. A swedish study published in 2012 sheds some light on this issue. For patients who are unsuitable for or who decline anticoagulants, asa 81 mg daily is suggested.
It is used to determine whether or not treatment is required with anticoagulation therapy or antiplatelet therapy. A high chads 2 score corresponds to a greater risk of stroke, while a low chads 2. The canadian cardiovascular society states that a doac is the preferred choice.
The chads 2 score is a validated stroke risk assessment tool for patients with af that was first presented at the 2001 international stroke meeting.