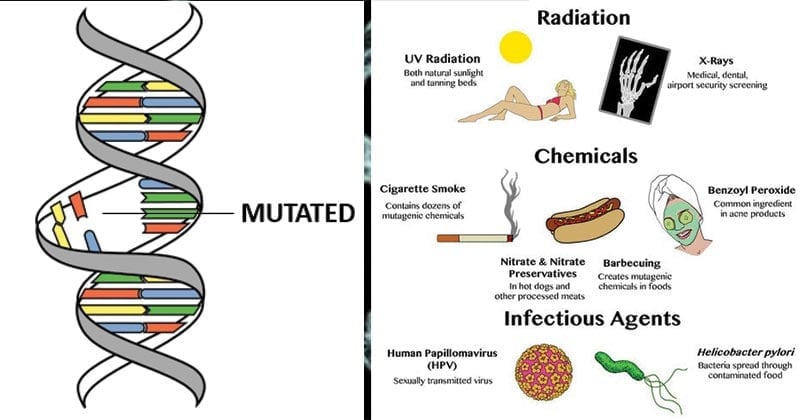
Mutations can occur during dna replication if errors are made and not corrected in time. Uv radiation on the other hand causes mild dna damage like pyrimidine dimer.
Mutations can also be caused by environmental foes.
Causes of dna mutation. Mutations can occur during dna replication if errors are made and not corrected in time. Certain compounds can mutate dna but won’t necessarily result in cancer. Nevertheless, when the cell repairs the dna, it might not do a perfect job of the repair.
A mutation is a change in a dna sequence. Chemicals that change normal base pairing can generate mutations by. One way these hazards attack our genes is very sneaky:
- change a base by covalent modification. Mutations can also be caused by environmental foes. Mutation rate variation across viruses.
Uv radiation on the other hand causes mild dna damage like pyrimidine dimer. How does sunlight cause mutations in dna? These alterations can be caused by environmental changes such as chemicals or uv rays and random mistake in dna replication.
Meanwhile, carcinogens are agents that cause cancer. Tobacco, ultraviolet light and other chemicals are all potential enemies of dna. “due to the replication errors, exposure to mutagens and viral infections changes or alterations occur in a dna sequence which causes genetic abnormalities, is known as mutation.”.
Mutations can also be caused by exposure to specific chemicals or radiation. This generates reactive oxygen species like singlet oxygen or hydrogen peroxide that oxidize the dna bases causing mutations. They have the ability to damage the chemicals making up dna.
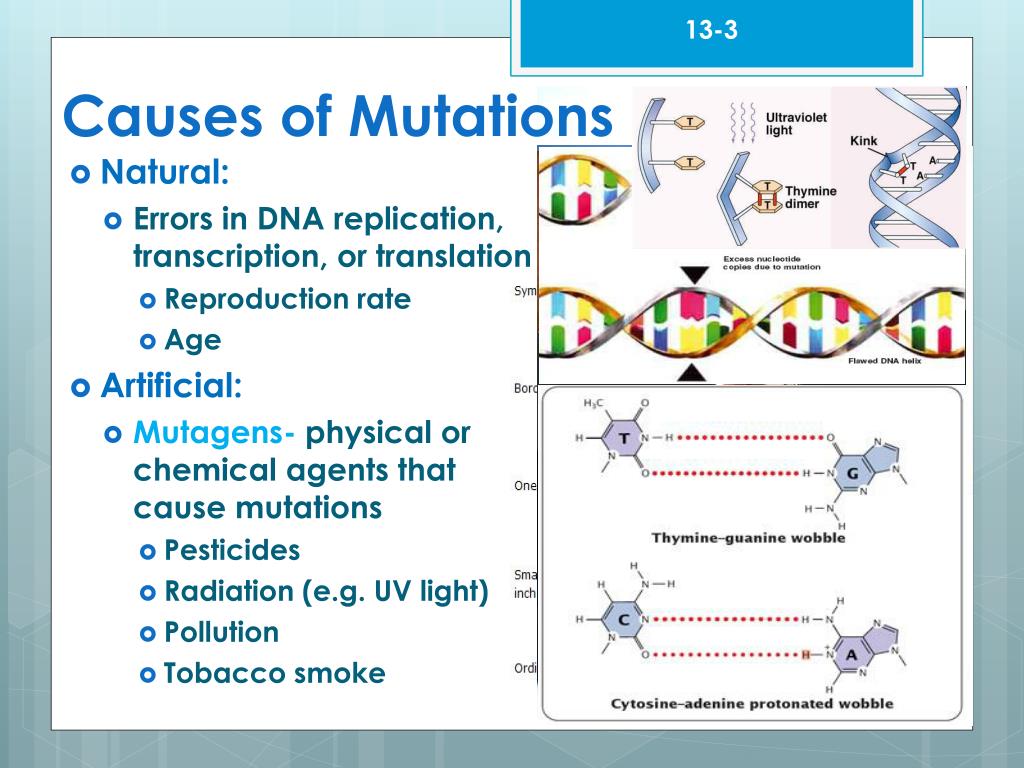
Mutations that do not occur during replication: Mutagens are external factors that can cause alterations to dna. Spontaneous mutations are heritable, random changes to the base sequence in the dna that result from natural phenomena.
These agents cause the dna to break down. 3) cause cross linking of dna strands. Carcinogens are mutagens that cause cancer such as uv radiation.
These can be caused by the changes in the dna helical structure or due to exposure to radiations. It is an alteration in a gene from its natural state. Mutations are permanent alteration occurring in our dna sequence.
The flipside is also true, there are carcinogens that don’t cause dna mutation. Mutations can result from dna copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or infection by viruses. These changes could result from errors made and not corrected by dna polymerase during replication or from.
Dna mutation occurs when there are changes in the nucleotide sequence that make up dna strand. This is not necessarily unnatural — even in the most isolated and pristine environments, dna breaks down. Mutagens are agents that cause dna mutations.
Ionisation radiation causes gene mutations like point, deletion and insertion mutations as well as dna strand breaks. 1) de aminating amino groups. These agents cause the dna to break down.
These mutations are caused by mutagens. Each cell, in order to function correctly, depends on thousands of proteins. Mutations may be caused by exposure to specific chemicals or radiation.
Mutations can also occur as the result of exposure to environmental factors such as smoking, sunlight and radiation. Which of the following is a cause of a dna mutation?