
Longo, m.d., and wyndham h. Car t cell related toxicity remains a clinical challenge.
A hostile tme is a strong barrier to.
Car t cells lymphoma. Unfortunately, normal b or t cells also express the majority of lymphoma target antigens suitable for car recognition. A hostile tme is a strong barrier to. T cells are removed from patients and genetically modified to produce cars.
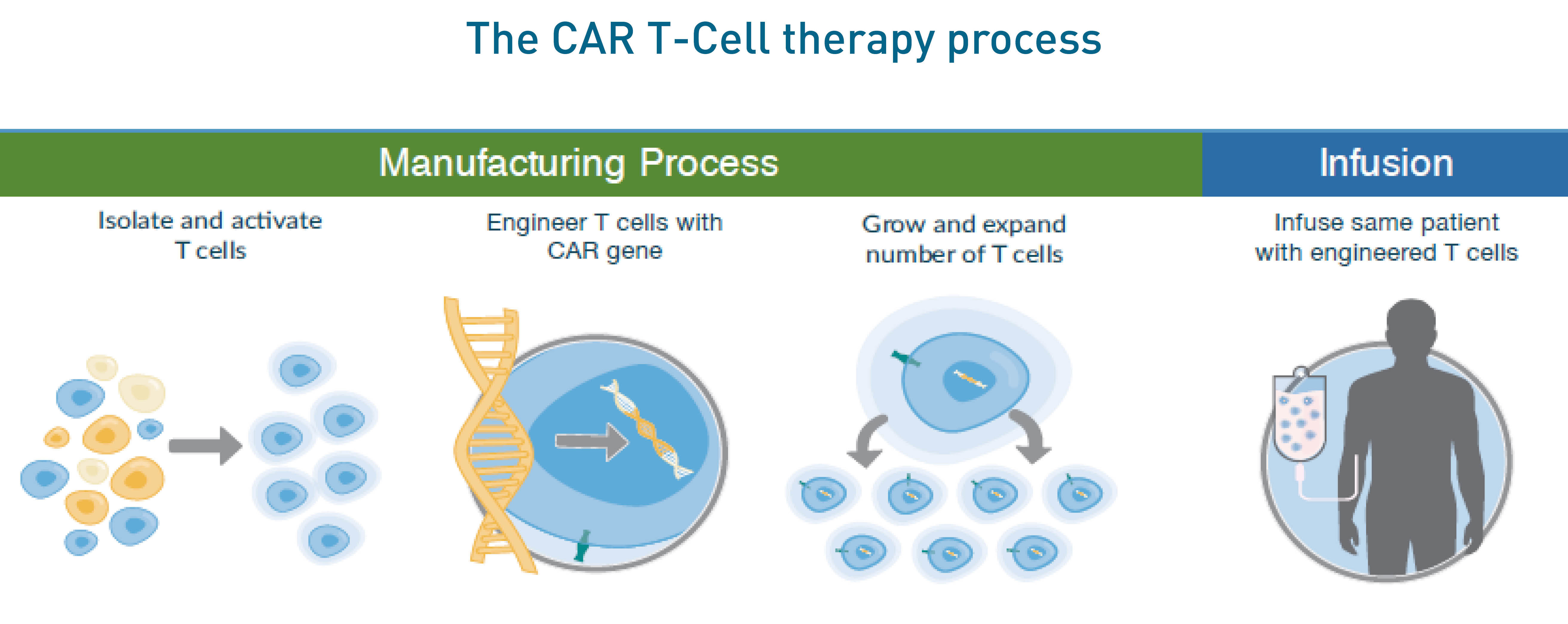
Car t cells induce a complete response in refractory burkitt lymphoma. Car t cell therapy provides engineered molecules called chimeric antigen receptors (cars) that recognize and destroy antigens present on the surface of lymphoma cells. The t cells are isolated and sent to a special laboratory where they are genetically modified with inactive viruses with a receptor that detect.
Car t cell related toxicity remains a clinical challenge. Car t cells are active in hodgkin lymphoma. Cutaneous t cell lymphomas (ctcl) are a heterogeneous group of malignancies characterized by the expansion of a malignant t cell clone.
Patients showing cr at 3 months have an 80% to 90% probability of remaining in response, and. The microenvironment of solid tumors often protects tumor cells from the immune system. Expressing chimeric antigen receptors (cars) on t cells is a means of.
Patients had disease that had relapsed or was refractory after the receipt of up to five previous. Immune cells or antibodies could be produced within the laboratory beneath tightly managed situations and then given to patients to treat most cancers. Lymphomas arise from clonal expansions of b, t, or nk cells at different stages of differentiation.
Mark roschewski, m.d., dan l. Longo, m.d., and wyndham h. The genetically engineered car t cells are grown in the laboratory until they number in the billions and are then infused back into the.
The phase 1/2 clinical trials that led to us food and drug administration approval excluded patients with central nervous system (cns) involvement, due to strict eligibility criteria. They have emerged as effective therapy in patients with multiple relapsed/refractory disease, capable of sustaining durable remissions.