Relapse after conventional chemotherapy remains a major problem in patients with myeloid malignancies such as acute myeloid leukemia (aml), and the major cause of death after diagnosis of aml is from relapsed disease. Whether car t cells will one day be able to vanquish solid tumors as effectively as they destroy blood cancers is a nagging question facing the field.

Chop researchers are also testing a car t cell that targets both cd19 and cd123, another antigen commonly found on leukemia cells.
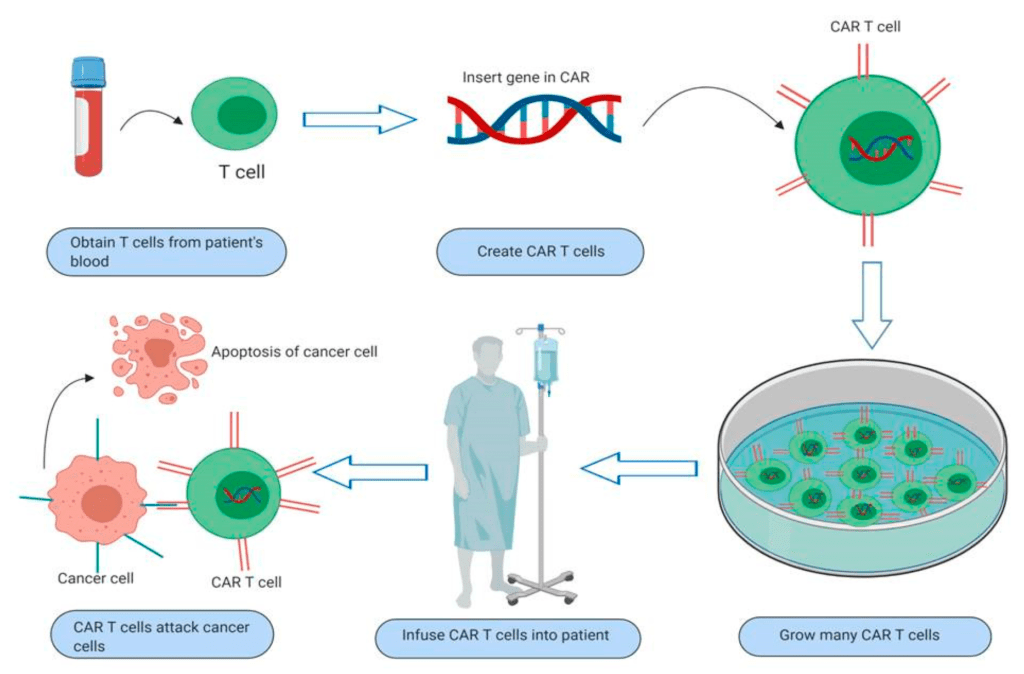
Car t cells leukemia. State of the art and future directions. The manufacturing process is the same in both cases; Early studies in animal models have suggested that this dual targeting may prevent antigen loss.
However, the loss of specific antigens, cell fratricide, t cell aplasia, and normal t cell separation are challenges in treating t cell leukemia/lymphoma with car t therapy. Scientists are also studying the effectiveness of experimental new bites that target proteins other than cd19 in malignant leukemic cells. Car t cells targeting cd19 are approved for patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all), failing two or more prior therapies.
The central nervous system (cns) is a known sanctuary site of all. They also mediated cancer remission. Memorial sloan kettering scientists played a pivotal role in developing the science and technology on which the newly approved treatment is based.
Only the choice of initial blood donor is. Cars have had the most success in treating blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. Successful treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (aml) with chimeric antigen receptor (car) t cells is hampered by toxicity on normal hematopoietic progenitor cells and low car t cell persistence.
Whether car t cells will one day be able to vanquish solid tumors as effectively as they destroy blood cancers is a nagging question facing the field. Car t cells for acute myeloid leukemia: This may be related to abundant cd19 expression on residual leukemia in these patients, in contrast to low or absent levels of cd19 in patients with mrd ( 22 ), or a.
Chop researchers are also testing a car t cell that targets both cd19 and cd123, another antigen commonly found on leukemia cells. Therewith, aml xenograft model survival was lengthened by the effect of flt3l car t cell. Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) is currently approved to treat children and young adults with leukemia.
This includes antithymocyte globulin (atg) formulations. Relapse after conventional chemotherapy remains a major problem in patients with myeloid malignancies such as acute myeloid leukemia (aml), and the major cause of death after diagnosis of aml is from relapsed disease. The designer t cells not only expanded, persisted, and attacked tumor cells after transfer into patients;
1 allogeneic car t cells offer possible advantages compared to autologous car t cell therapies. Such car t cells have shown great promise in beating back blood cancers, such as several types of leukemia and lymphoma, that have stopped responding to other therapies. Chimeric antigen receptor t (car t) cells are widely being investigated for their ability to treat certain malignancies, in particular leukemias and lymphomas.
Some worry that cd19 may be unique as a target, and that the approach might not work for other cancers. It is approved for children and young adults up to 25 years of age who relapsed or did not respond to therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all).