From the point of view of etiology, clinical features, and visual outcome, it can be. Occlusion can affect a branch of the retinal artery as well as the central retinal artery.

Neovascularization (abnormal new vessel formation) of the retina or iris (rubeosis iridis) with secondary (neovascular) glaucoma occurs in about 20%.
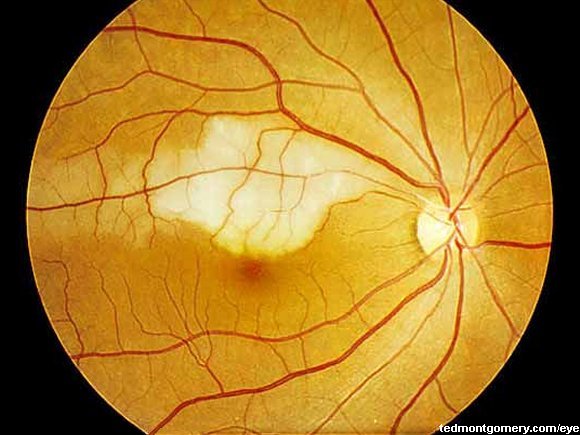
Branch retinal arterial occlusion. There are two types of raos: Baumal, in atlas of retinal oct: Branch retinal artery occlusion (brao) results from obstruction of one of the branches of the central retinal artery.
Branch retinal artery occlusion (brao) blocks the small arteries, that branch off the central artery. In central retinal artery occlusion, the patient generally complains of sudden, painless unilateral blindness. Submit your research to this special issue by journal of ophthalmology.
The macula can swell from this fluid, affecting your central vision. Let’s review just a few pearls of branch retinal artery occlusions. Occlusion of the central retinal artery (crao), a branch of the central retinal artery (brao), or the cilioretinal artery (clrao) may occur.
A lack of oxygen flow to the retina will cause a sudden retinal disease which is an emergency due dramatic vision loss. Therefore, the universally used term “branch retinal artery occlusion” is incorrect. The sensitive neural tissue of the retina is highly dependent on adequate blood flow;
There are two types of raos: Occlusion can affect a branch of the retinal artery as well as the central retinal artery. New insights and future perspectives.
There are vascular occlusions (blockage of blood flow) of the r etinal veins and vascular occlusions of the retinal arteries. Md mba, fasrs, fpcs, fpao. In branch retinal artery occlusion, the patient will notice a loss of visual acuity or visual field defects.
Artery occlusions occur after a blood vessel is completely blocked by an object, called an embolus. In a young patient with no history of cardiovascular risk factors who develops retinal arterial occlusion, other causes such as hypercoagulable syndromes must be excluded. They typically present with monocular vision loss and a relative visual field defect.
First, it is felt that brao’s comprise 38% of all acute retinal artery obstructions. It is caused due to reduced or. There are two general classes of retinal vascular occlusions.
The most common cause is emboli secondary to either carotid plaques or cardiac. A branch retinal artery occlusion usually occurs at the junction of two smaller arteries, where blood flow is disrupted and an area of ischemia occurs. The cause of a branch retinal artery occlusion is often caused by a plaque, calcium, or platelet deposit becoming lodged at an arterial bifurcation in the.
Branch retinal artery occlusion (brao) blocks the small arteries in your retina. When the vein is blocked, blood and fluid spills out into the retina. When branches of the retinal vein become blocked, it is called branch retinal vein occlusion (brvo).
This is similar to a stroke. Optical coherence tomography, 2018 summary. Central retinal artery occlusion (crao) is a blockage in the central artery in your retina.
The eye’s retina has one main artery and one main vein. Neovascularization (abnormal new vessel formation) of the retina or iris (rubeosis iridis) with secondary (neovascular) glaucoma occurs in about 20%. New insights and future perspectives.
Branch retinal arteriolar occlusion (brao) is a common ocular vascular occlusive disorder. From the point of view of etiology, clinical features, and visual outcome, it can be. A retinal artery occlusion (rao) is a blockage in one or more of the arteries of your retina.
She had a positive severe acute respiratory. Submit your research to this special issue by journal of ophthalmology. Less common, nonembolic causes include vasospasm and inflammatory and.
Pedgaz > branch retinal artery occlusion description retinal artery occlusions may arise where atheromatous emboli break free, most often in the carotid artery, and travel in the bloodstream to cause a blockage downstream. Therefore occlusion of one of these arteries can have profound visual effects resulting in transiet or permanent visual field loss [1, 2].