Beta blockers in systolic heart failure. Other beta blockers, such as labetalol (normodyne), atenolol (tenormin) and propranolol (inderal), have not been.

Know how and when to start therapy and how to titrate the dose.
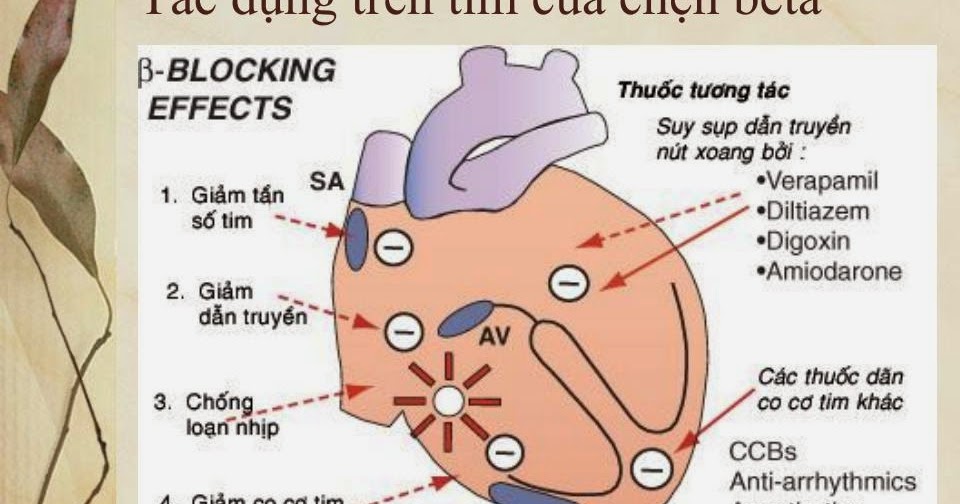
Beta blockers used in heart failure. They also can stop your heart from responding to stress hormones, such as adrenaline. Beta blockers help your heart beat more slowly and lower your blood pressure, thus protecting your heart from the harmful effects of prolonged adrenaline and noradrenaline activity. “some β blocker is better than no β blocker” in recent decades, important gains have been made in the treatment of chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.1 β blockers are a cornerstone of the medical management of heart failure.
1 2 3 as a result, these agents are now recommended for use in all patients with mild to moderate heart failure caused by left ventricular (lv) systolic dysfunction who do not have contraindications. There seems to be a class effect; Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2021, issue 7.
By slowing the heart rate, the symptoms caused by af, particularly palpitations and fatigue, are often improved. However, people with moderate or severe heart failure may need to start with a low dose, which is then increased slowly. With progressive dose increment, tolerance of such treatment was generally good, left ventricular function improved, hospitalisations for heart failure were less frequent and mortality was reduced.
Then titrate the dosage slowly Safi s, korang sk, nielsen ee, sethi nj, feinberg j, gluud c, jakobsen jc. The long term use of certain β blockers in patients with heart failure reduces hospital.
Yancy 2013), or in patients classified with mild to. However, to date, they are underused, mainly because of the misconception that hypotension. Therefore, on the basis of available evidence, a β blocker should still be regarded as the safest drug for heart rate control in patients with heart failure, reduced ejection fraction, and atrial fibrillation.
Other beta blockers, such as labetalol (normodyne), atenolol (tenormin) and propranolol (inderal), have not been. Current guidelines from accf/aha recommend the use of beta‐blockers in all patients with reduced lvef and heart failure corresponding to stage b or c, or both (accf/aha) regardless of whether they are with or without a history of myocardial infarction (see table 2) (dunlay 2014; Beta blockers are used to control the irregular heart rhythm in people with atrial fibrillation (af).
Not all beta blockers are equally tolerated by patients with chronic heart failure. However, underuse of this class of drugs is still. Beta blockers are an important part of managing heart failure.
A substantial database has accumulated over the last 20 years supporting the benefits of these agents on ventricular function and clinical status. Beta blockers in systolic heart failure. Beta blockers should now be considered standard therapy in patients with new york heart association class ii or class iii heart failure who are hemodynamically stable, who do not have dyspnea at.
Why beta blockers are not used in acute heart failure? Start together with ace inhibitor as soon as chf is diagnosed initiate at low dose when chf with reduced ejection fraction is stable; Treatment of some heart rhythm disorders.
Know how and when to start therapy and how to titrate the dose.