Epinephrine or norepinephrine can displace bound beta blockers if they’re in higher concentration. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure.
Beta blockers | mechanism of action, indications, adverse reactions, contraindications.
Beta 2 blockers mechanism of action. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists of catecholamines. Mol pharmacol., 64 (2003), pp. Mechanism of action of beta blockers.
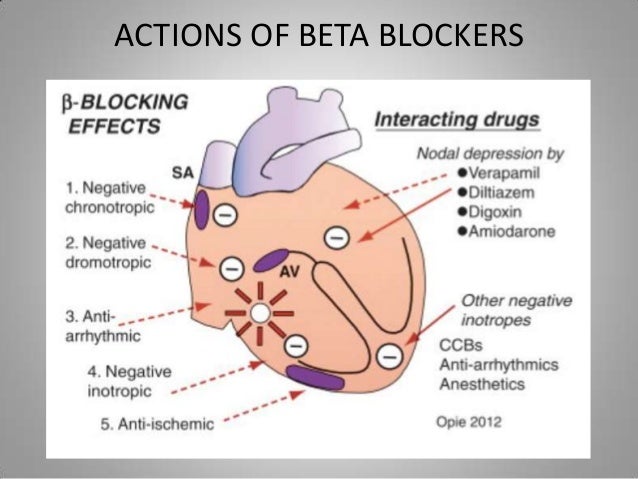
Beta blocker toxicity can also occur through indirect mechanisms such as sodium and calcium channel blockade. They differ in their receptor selectivity, intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (isa), vasodilating properties and metabolism. Beta blockers antagonize the sympathetic fight.
During this lecture professor zach murphy will go into detail on how beta blockers are used to lower and control high blood pressure. Furthermore, what is the beta blockers mechanism of action? Tegan evans, davis maclean, yan yu* reviewers:, amanda nguyen, p.
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers | mechanism of action, indications, adverse reactions, contraindications. Beta blockers also help open up your veins and arteries to improve blood flow.
The alpha receptor is divided into two types, alpha 1 and alpha 2, based on response to. The list of beta blocker drugs is extensive making the mechanism of action and pharmacology challenging. Mechanism of action, blood pressure control, and effects of lipoprotein metabolism.
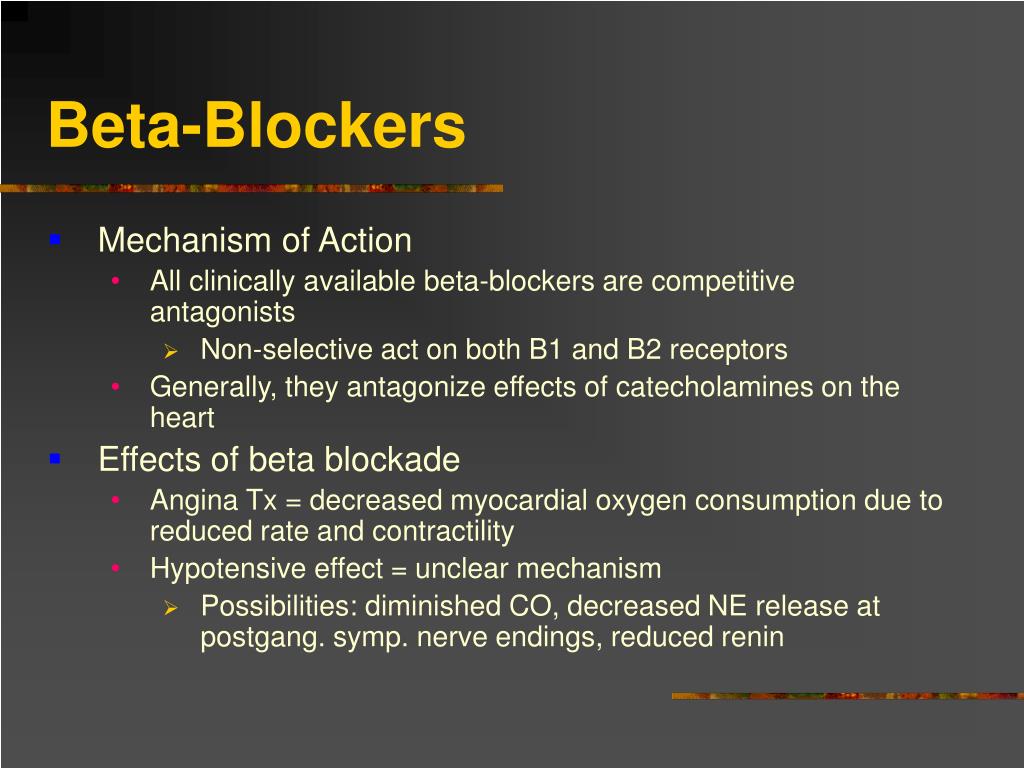
See link for full description of beta blockers. They block beta 1 receptors and are very useful in hypertension and certain cardiac diseases. They relax the heart and slow its pumping, thus lowering blood pressure and heart rate.
Antihypertensive mechanisms and effect differ according. Therefore, the chronotropic and inotropic effects on the heart undergo inhibition, and the heart rate slows down as a result. Patient was educated on nonselective beta blockers and mechanism of action used for management of hypertension as follows:
Timothy pollak*, sean spence* * md at time of publication beta blockers bind to beta 1. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure. They bind to the same receptors without activating them, preventing catecholamines to initiate their function.
The sympathetic nervous system plays a major role in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension and is mediated by the alpha and beta receptors. The term ‘mechanism of action’ is used with reference to the specific biochemical interaction that helps a drug produce its pharmacological effect. Beta blockers cause your heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure.
Affinity is the ability of a drug to bind the receptor, and efficacy is the ability to induce a response. Epinephrine or norepinephrine can displace bound beta blockers if they’re in higher concentration. This will include a brief discussion on the pathophysiology of hypertension (htn) and how beta blockers target.
Certain beta blockers including propranolol and labetalol also exhibit membrane. Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline.