
While b cells produce the antibodies that target diseased cells, t cells directly destroy bacteria or cells infected with viruses. The main difference between t cells and b cells is that t cells can only recognize viral antigens outside the infected cells whereas b cells can recognize the surface antigens of bacteria and viruses.
They are one of the two types of lymphocytes;
B cells vs t cells. The precursors of t cells are also produced in the bone marrow but leave the bone marrow and mature in the t. There are many more t cells than b cells. While b cells produce the antibodies that target diseased cells, t cells directly destroy bacteria or cells infected with viruses.
B lymphocytes (often simply called b cells) and t lymphocytes (likewise called t cells). B cells are produced in the b one marrow. They are named as such because they are able to induce a humoral response in organisms that lack t cells.
The main function of b cells is to produce antibodies against pathogens. The main difference between t cells and b cells is that t cells can only recognize viral antigens outside the infected cells whereas b cells can recognize the. Hence, these cells are a component of the adaptive immunity.
(8, 9, and 10) what they fight against? B cells are the foundation of humoral immunity. B cells and t cells are the white blood cells of the immune system that are responsible for adaptive immune response in an organism.
Lymphokines vs antibodies and affinity maturation of b cell antigen receptors vs upregulation of adhesion molecules on t cells. B lymphocytes collect in tighter groups. The b cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies (abs).
Different types of leukocytes with different functions are present in the human body. Even b cell have surface receptors, while t cells do not. B cells and t cells are the major leukocytes which involve.
The lymphocytes also learn to recognize a specific antigen and bind to it. They are one of the two types of lymphocytes; One type, known as t helper cells, coordinate the body�s various immune responses.
B cells are a type of white blood cells in the circulation. T cells make up around 80% of all circulating lymphocytes. Thus, humoral immunity depends on.
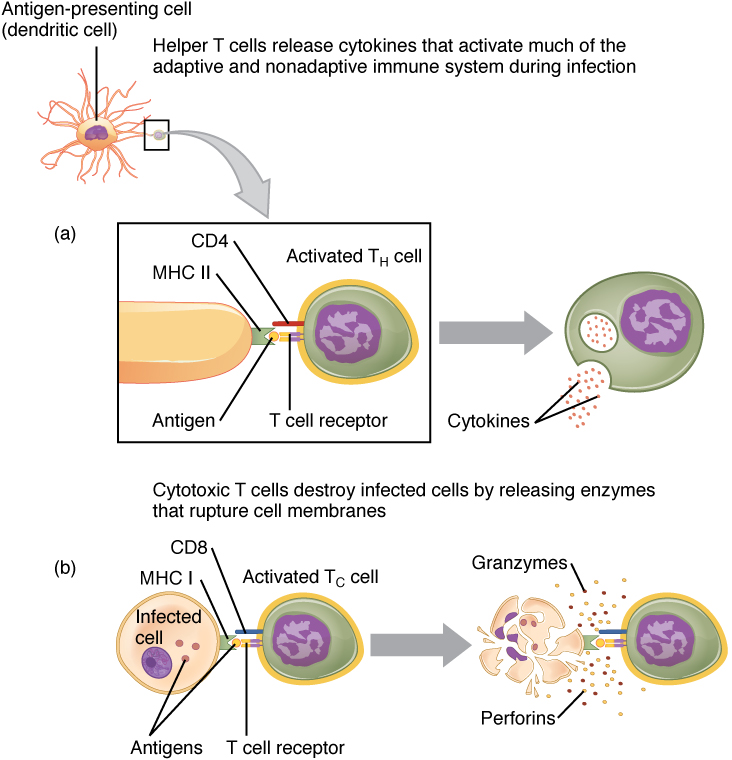
T cells have the longer lifespan (from days to weeks) as compare to b cells, which have short life lasting for few days to the week. Although memory t and b cells use different mechanisms to elaborate memory, there are a number of interesting analogies: Cd8+ cytotoxic t cells, on the other hand, directly kill infected cells.
T lymphocytes tend to be more diffusely distributed in the lymph nodes; However, the absence of specific antibodies in the serum does not necessarily mean an absence of immune memory. B cells mature in the bone marrow while the t.
B cells and t cells are both lymphocytes, or white blood cells produced in bone marrow and maturing in the organs of the body�s lymphatic system. Both the cells are made in the bone marrow. The main difference between t cells and b cells is that t cells can only recognize viral antigens outside the infected cells whereas b cells can recognize the surface antigens of bacteria and viruses.
During maturation, the lymphocytes learn to differentiate between foreign cells and self. B cell response to these antigens is rapid, though antibodies generated tend to have lower affinity and are less functionally versatile than. In the bloodstream, t cells occupy 80%, and b cells occupy remaining 20% of the total lymphocytes present in the blood.
B cells are also less abundant compared to t cells, only making up about 20 percent of the total blood lymphocytes. T lymphocyte is the second type of lymphocytes. Different types of pathogens require distinct immune effector cell types to be controlled.
The cytokines prime the maturation of b cells, which become plasma cells and produce antibodies to neutralise the pathogen. The second, called cytotoxic t cells or killer t cells,.